Supporting safe areas
By default, React Navigation aids in ensuring your application displays correctly on the iPhone X and other devices with notches and "safe areas". It does so by using SafeAreaView inside of UI elements that may interact with the sensor cluster ("the notch") or the home activity indicator.
The goal is to (a) maximize usage of the screen (b) without hiding content or making it difficult to interact with by having it obscured by a physical display cutout or some operating system UI.
It's tempting to solve (a) by wrapping your entire app in a container with padding that ensures all content will not be occluded. But in doing so, we waste a bunch of space on the screen, as pictured in the image on the left below. What we ideally want is the image pictured on the right. We can use SafeAreaView for this. The rest of this guide gives more information on how to support safe areas in React Navigation.
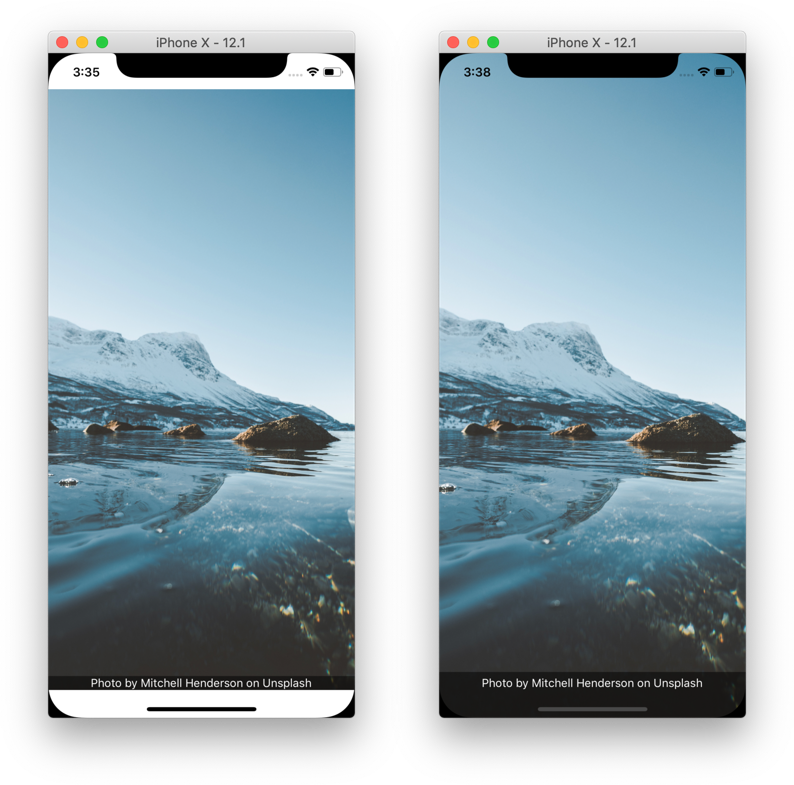
→ Run the example pictured on the left or, preferably, run the example pictured on the right.
Hidden/Custom Navigation Bar or Tab Bar

However, if you're overriding the default navigation bar, it's important to ensure your UI doesn't interfere with either of those hardware elements.
For example, if I render nothing for the header or tabBarComponent, nothing renders
const Tabs = createBottomTabNavigator({
...
}, {
tabBarComponent: () => null,
});
export default createStackNavigator({
...
}, {
headerMode: 'none',
});

To fix this issue you can wrap your content in a SafeAreaView, which can be imported from react-navigation. Recall that SafeAreaView should not wrap entire navigators, just the screen components or any content in them.
import { SafeAreaView } from 'react-navigation';
class MyHomeScreen extends Component {
render() {
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.paragraph}>This is top text.</Text>
<Text style={styles.paragraph}>This is bottom text.</Text>
</SafeAreaView>
);
}
}

This will detect if the app is running on an iPhoneX and, if so, ensure the content isn't hidden behind any hardware elements.
Landscape Mode
Even if you're using the default navigation bar and tab bar if your application works in landscape mode it's important to ensure you content isn't hidden behind the sensor cluster.
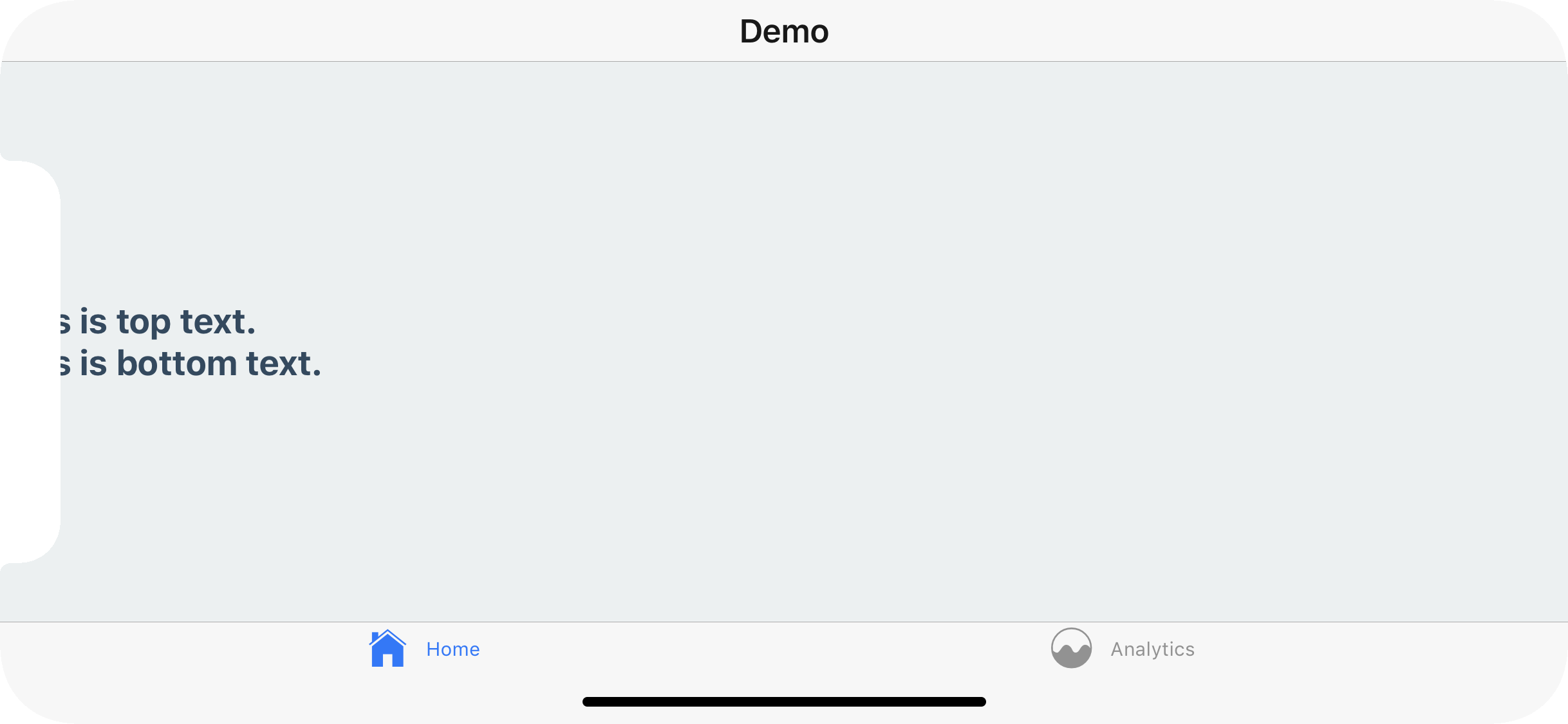
To fix this you can, once again, wrap your content in a SafeAreaView. This will not conflict with the navigation bar nor the tab bar's default behavior in portrait mode.
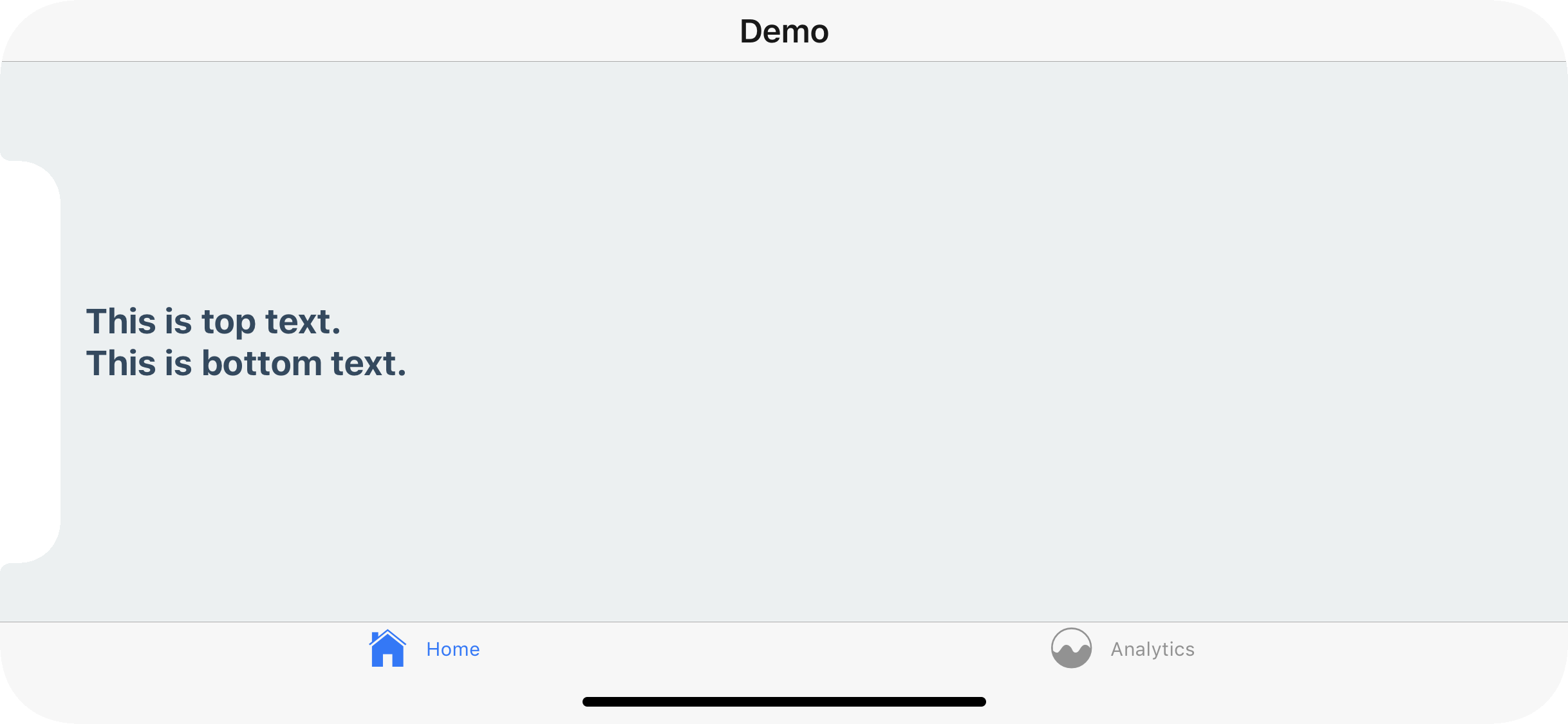
In conclusion, use the SafeAreaView component on the screens you register with a React Navigation navigator.
A Snack is available with the code used in this overview.
Use forceInset to get more control
In some cases you might need more control over which paddings are applied. For example, you can remove bottom padding by passing forceInset prop to SafeAreaView.
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container} forceInset={{ bottom: 'never' }}>
<Text style={styles.paragraph}>This is top text.</Text>
<Text style={styles.paragraph}>This is bottom text.</Text>
</SafeAreaView>
forceInset takes an object with the keys top | bottom | left | right | vertical | horizontal and the values 'always' | 'never'. Or you can override the padding altogether by passing an integer.
There is also a Snack available to demonstrate how forceInset behaves.
Android notches
React Native does not currently expose an API to access information about device cutouts on Android devices. If your app has an opaque status bar (the default in React Native), that may handle the area where the device has its cutout without any further work required. If not, to workaround this you may want to use the following temporary workaround:
- Install react-native-device-info.
- Check if the device has a notch with
DeviceInfo.hasNotch()- this compares the device brand and model to a list of devices with notches - a crude but effective workaround. - If the device has a notch, you may want to increase the status bar height known to the SafeAreaView by doing something like this:
import { Platform } from 'react-native';
import { SafeAreaView } from 'react-navigation';
import DeviceInfo from 'react-native-device-info';
if (Platform.OS === 'android' && DeviceInfo.hasNotch()) {
SafeAreaView
.setStatusBarHeight
/* Some value for status bar height + notch height */
();
}
Work is in progress on a longer term solution, see this pull request for more information.